Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ishikawa, Norito; Fukuda, Shoma; Nakajima, Toru; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Fujimura, Yuki; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*
Materials, 17(3), p.547_1 - 547_21, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.04(Chemistry, Physical)Natural monoclinic zirconia (baddeleyite) was irradiated with 340-MeV Au ions, and the irradiation-induced nanostructures (i.e., ion tracks and nanohillocks) were observed using transmission electron microscopy. The diameter of the nanohillocks is approximately 10 nm, which is similar to the maximum molten region size calculated using the analytical thermal spike model. Ion tracks are imaged as strained regions that maintain their crystalline structure. The cross-sections of most of the ion tracks are imaged as parallelopiped or rectangular contrasts as large as 10 nm. These results strongly indicate that the molten region is recrystallized anisotropically, reflecting the lattice structure. Furthermore, low-density track cores are formed in the center of the ion tracks. The formation of low-density track cores can be attributed to the ejection of molten matter toward the surface.
Amekura, Hiroshi*; Chettah, A.*; Narumi, Kazumasa*; Chiba, Atsuya*; Hirano, Yoshimi*; Yamada, Keisuke*; Yamamoto, Shunya*; Leino, A. A.*; Djurabekova, F.*; Nordlund, K.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.1786_1 - 1786_10, 2024/02
Injecting high-energy heavy ions in the electronic stopping regime into solids can create cylindrical damage zones called latent ion tracks. Although these tracks form in many materials, none have ever been observed in diamond, even when irradiated with high-energy GeV uranium ions. Here we report the first observation of ion track formation in diamond irradiated with 2-9 MeV C fullerene ions. Depending on the ion energy, the mean track length (diameter) changed from 17 (3.2) nm to 52 (7.1) nm. High resolution scanning transmission electron microscopy (HR-STEM) indicated the amorphization in the tracks, in which
fullerene ions. Depending on the ion energy, the mean track length (diameter) changed from 17 (3.2) nm to 52 (7.1) nm. High resolution scanning transmission electron microscopy (HR-STEM) indicated the amorphization in the tracks, in which  -bonding signal from graphite was detected by the electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS).
-bonding signal from graphite was detected by the electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS).
Iwase, Akihiro*; Fukuda, Kengo*; Saito, Yuichi*; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Semboshi, Satoshi*; Amekura, Hiroshi*; Matsui, Toshiyuki*
Journal of Applied Physics, 132(16), p.163902_1 - 163902_10, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Applied)Amorphous SiO samples were implanted with 380 keV Fe ions at room temperature. After implantation, some of the samples were irradiated with 16 MeV Au ions. magnetic properties were investigated using a SQUID magnetometer, and the morphology of the Fe-implanted SiO
samples were implanted with 380 keV Fe ions at room temperature. After implantation, some of the samples were irradiated with 16 MeV Au ions. magnetic properties were investigated using a SQUID magnetometer, and the morphology of the Fe-implanted SiO samples was examined using transmission electron microscopy and X-ray absorption spectroscopy (EXAFS and XANES), which showed that the size of Fe nanoparticles was increasing The size of Fe nanoparticles increased with increasing Fe implantation amount; some of the Fe nanoparticles consisted of Fe oxides, and the valence and structure of Fe atoms became closer to that of metallic
samples was examined using transmission electron microscopy and X-ray absorption spectroscopy (EXAFS and XANES), which showed that the size of Fe nanoparticles was increasing The size of Fe nanoparticles increased with increasing Fe implantation amount; some of the Fe nanoparticles consisted of Fe oxides, and the valence and structure of Fe atoms became closer to that of metallic  -Fe with increasing Fe injection amount. The magnetization-field curve of the sample implanted with a small amount of Fe was reproduced by Langevin's equation, suggesting that the Fe nanoparticles behave in a superparamagnetic manner. In addition, when a large amount of Fe was implanted, the magnetization-magnetic field curve shows a ferromagnetic state. These magnetic property results are consistent with the X-ray absorption results. Subsequent 16 MeV Au irradiation crushed the Fe nanoparticles, resulting in a decrease in magnetization.
-Fe with increasing Fe injection amount. The magnetization-field curve of the sample implanted with a small amount of Fe was reproduced by Langevin's equation, suggesting that the Fe nanoparticles behave in a superparamagnetic manner. In addition, when a large amount of Fe was implanted, the magnetization-magnetic field curve shows a ferromagnetic state. These magnetic property results are consistent with the X-ray absorption results. Subsequent 16 MeV Au irradiation crushed the Fe nanoparticles, resulting in a decrease in magnetization.
 Fe
Fe O
O /Pt heterostructures
/Pt heterostructuresIeda, Junichi; Okayasu, Satoru; Harii, Kazuya*; Kobata, Masaaki; Yoshii, Kenji; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Ishida, Masahiko*; Saito, Eiji
IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 58(8), p.1301106_1 - 1301106_6, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:22.45(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)The combination of spin-driven thermoelectric (STE) devices based on spin Seebeck effect (SSE), and radioactive isotopes as heat sources, has potential as a next-generation method of power generation in applications such as power supplies for space probes. However, there has been very limited knowledge available indicating the irradiation tolerance of spin thermoelectric devices. Through analysis using a heavy ion-beam accelerator and the hard X-ray photoemission spectroscopy (HAXPES) measurements, we show that a prototypical STE device based on Y Fe
Fe O
O /Pt heterostructures has tolerance to irradiation of high-energy heavy-ion beams. We used 320 MeV gold ion beams modeling cumulative damages due to fission products emitted from the surface of spent nuclear fuels. By varying the dose level, we confirmed that the thermoelectric and magnetic properties of the SSE elements are not affected by the ion-irradiation dose up to
/Pt heterostructures has tolerance to irradiation of high-energy heavy-ion beams. We used 320 MeV gold ion beams modeling cumulative damages due to fission products emitted from the surface of spent nuclear fuels. By varying the dose level, we confirmed that the thermoelectric and magnetic properties of the SSE elements are not affected by the ion-irradiation dose up to 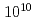 ions/cm
ions/cm fluence and that the SSE signal is extinguished around
fluence and that the SSE signal is extinguished around 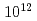 ions/cm
ions/cm , in which the ion tracks almost fully cover the sample surface. In addition, the HAXPES measurements were performed to understand the effects at the interface of Y
, in which the ion tracks almost fully cover the sample surface. In addition, the HAXPES measurements were performed to understand the effects at the interface of Y Fe
Fe O
O /Pt. The HAXPES measurements suggest that the chemical reaction that diminishes the SSE signals is enhanced with the increase of the irradiation dose. We share the current understandings of the damage analysis in Y
/Pt. The HAXPES measurements suggest that the chemical reaction that diminishes the SSE signals is enhanced with the increase of the irradiation dose. We share the current understandings of the damage analysis in Y Fe
Fe O
O /Pt for developing better STE devices applicable to harsh environmental usages.
/Pt for developing better STE devices applicable to harsh environmental usages.
 irradiated with swift heavy ions at grazing incidence
irradiated with swift heavy ions at grazing incidenceIshikawa, Norito; Fujimura, Yuki; Kondo, Keietsu; Szabo, G. L.*; Wilhelm, R. A.*; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*
Nanotechnology, 33(23), p.235303_1 - 235303_10, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:48.5(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)A single crystal of SrTiO doped with niobium (Nb-STO) was irradiated with 200 MeV Au ions at grazing incidence. Atomic force microscopy (AFM) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) are used to study the relation between irradiation-induced change of surface topography and corresponding material property changes. As expected, multiple hillocks as high as 5-6 nm are imaged by AFM observation. It is also found that the region in between the adjacent hillocks is slightly elevated rather than depressed. Line-like contrasts along the ion paths are found in both AFM phase images and SEM images, indicating the formation of continuous ion tracks in addition to multiple hillocks. Cross-sectional transmission electron microscopy (TEM) observation shows that the ion tracks in the near-surface region are found to be relatively large, whereas buried ion tracks in the deeper region are relatively small. The results suggest that recrystallization plays an important role in the formation of small ion tracks in the deep region, whereas formation of large ion tracks in the near-surface region is likely due to the absence of recrystallization.
doped with niobium (Nb-STO) was irradiated with 200 MeV Au ions at grazing incidence. Atomic force microscopy (AFM) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) are used to study the relation between irradiation-induced change of surface topography and corresponding material property changes. As expected, multiple hillocks as high as 5-6 nm are imaged by AFM observation. It is also found that the region in between the adjacent hillocks is slightly elevated rather than depressed. Line-like contrasts along the ion paths are found in both AFM phase images and SEM images, indicating the formation of continuous ion tracks in addition to multiple hillocks. Cross-sectional transmission electron microscopy (TEM) observation shows that the ion tracks in the near-surface region are found to be relatively large, whereas buried ion tracks in the deeper region are relatively small. The results suggest that recrystallization plays an important role in the formation of small ion tracks in the deep region, whereas formation of large ion tracks in the near-surface region is likely due to the absence of recrystallization.
Ishikawa, Norito; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*; Okubo, Nariaki
Shototsu, 18(3), p.43 - 55, 2021/05
Radiation damage mechanism in ceramics irradiated with swift heavy ions has been studied by using transmission electron microscopy (TEM). We introduce how the mechanisms are unveiled by our recent TEM studies.
 superconductors
superconductorsSueyoshi, Tetsuro*; Enokihata, Ryusei*; Hidaka, Yuka*; Irie, Masahiro*; Fujiyoshi, Takanori*; Okuno, Yasuki*; Ishikawa, Norito
Physica C, 582, p.1353824_1 - 1353824_5, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:7.92(Physics, Applied)We investigated the combined effect of flux pinning by three-directional columnar defects (CDs) in a wide field-angular range of YBa Cu
Cu Oy thin films, where CDs parallel to the
Oy thin films, where CDs parallel to the  -axis and CDs crossing at
-axis and CDs crossing at 
 (
( =45
=45 , 60
, 60 and 80
and 80 ) relative to the c-axis were installed by 200 MeV Xe-ion irradiations. The three-directional CDs with
) relative to the c-axis were installed by 200 MeV Xe-ion irradiations. The three-directional CDs with 

 60
60 form a field angular curve of critical current density Jc with a broad peak centered at magnetic field (B) parallel to the
form a field angular curve of critical current density Jc with a broad peak centered at magnetic field (B) parallel to the  -axis, whereas the Jc shows no peaks around the crossing angles of
-axis, whereas the Jc shows no peaks around the crossing angles of 
 . When the crossing angle is expanded to
. When the crossing angle is expanded to  =
= 80
80 , a drastic change in the field- angular behavior of Jc is induced: there is not a large enhancement of
, a drastic change in the field- angular behavior of Jc is induced: there is not a large enhancement of  around B//c. We also demonstrated that the combined configuration consisting of CDs at
around B//c. We also demonstrated that the combined configuration consisting of CDs at  = 0
= 0 ,
,  45
45 ,
,  60
60 and
and  80
80 provides a uniform enhancement of
provides a uniform enhancement of  over a wide angular-region.
over a wide angular-region.
Amekura, Hiroshi*; Toulemonde, M.*; Narumi, Kazumasa*; Li, R.*; Chiba, Atsuya*; Hirano, Yoshimi*; Yamada, Keisuke*; Yamamoto, Shunya*; Ishikawa, Norito; Okubo, Nariaki; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 11(1), p.185_1 - 185_11, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:75.03(Multidisciplinary Sciences)We report the track formation of 10 nm in diameter in silicon irradiated with 6 MeV C , i.e., much lower energy than the previously reported energy threshold.
, i.e., much lower energy than the previously reported energy threshold.
Ishikawa, Norito; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*; Ogawa, Hiroaki
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 4(4), p.43_1 - 43_14, 2020/12
Amorphizable ceramics were irradiated with 200 MeV Au ions, and the as-irradiated samples were observed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The ion track diameter and hillock diameter are similar for all the amorphizable ceramics. For SrTiO and niobium-doped STO, 200 MeV Au ion irradiation and TEM observation were also performed. The ion track diameters in these materials are found to be markedly smaller than the hillock diameters. The ion tracks in these materials exhibit inhomogeneity, which is similar to that reported for non-amorphizable ceramics. On the other hand, the hillocks appear to be amorphous, and the amorphous feature is in contrast to the crystalline feature of hillocks observed in non-amorphizable ceramics. No marked difference is recognized between the nanostructures in STO and those in Nb-STO.
and niobium-doped STO, 200 MeV Au ion irradiation and TEM observation were also performed. The ion track diameters in these materials are found to be markedly smaller than the hillock diameters. The ion tracks in these materials exhibit inhomogeneity, which is similar to that reported for non-amorphizable ceramics. On the other hand, the hillocks appear to be amorphous, and the amorphous feature is in contrast to the crystalline feature of hillocks observed in non-amorphizable ceramics. No marked difference is recognized between the nanostructures in STO and those in Nb-STO.
Amekura, Hiroshi*; Li, R.*; Okubo, Nariaki; Ishikawa, Norito; Chen, F.*
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 4(4), p.39_1 - 39_11, 2020/12
Evolution of depth profiles of the refractive index in Y Al
Al O
O (YAG) crystals were studied under 200 MeV Xe ion irradiation. The index changes were observed at three different depth regions; (i) a plateau near the surface between 0 and 3
(YAG) crystals were studied under 200 MeV Xe ion irradiation. The index changes were observed at three different depth regions; (i) a plateau near the surface between 0 and 3  m in depth, which can be ascribed to the electronic stopping Se, (ii) a broad peak at 6
m in depth, which can be ascribed to the electronic stopping Se, (ii) a broad peak at 6  m in depth, and (iii) a sharp dip at 13
m in depth, and (iii) a sharp dip at 13  m in depth, which is attributed to the nuclear stopping Sn peak.
m in depth, which is attributed to the nuclear stopping Sn peak.
Tsuchida, Hidetsugu*; Kai, Takeshi; Kitajima, Kensei*; Matsuya, Yusuke; Majima, Takuya*; Saito, Manabu*
European Physical Journal D, 74(10), p.212_1 - 212_7, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:17.64(Optics)Fundamental study of interaction between biomolecules and heavy ions in water is very important to predict an initial stage of radiation biological effects. A heavy ion irradiation experiment into droplet target assumed as a biological system in a vacuum was performed to measure production yields of cations and anions for glycine, which was ejected from the droplet target to the vacuum. However, the production mechanisms have been unknown. The PHITS code adapting ion track structure mode was used to analyze the production mechanisms from the dose evaluation at the surface between the vacuum and the water. It is found that induction yields of ionization and excitation, and dissociative electron attachment involved in the secondary electrons were correlated with the production yields of cations and anions of the glycine. The results provide us newly scientific insights to predict an initial stage of radiation biological effects.
 by using Poisson distribution function
by using Poisson distribution functionYamamoto, Yuki*; Ishikawa, Norito; Hori, Fuminobu*; Iwase, Akihiro*
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 4(3), p.26_1 - 26_13, 2020/09
The lattice constant and the magnetic state of CeO are modified by the irradiation with 200 MeV Xe ions. Under the assumption that these modifications are induced in the narrow one-dimensional region (the ion track) along the ion beam path, the dependence of the lattice constant and the saturation magnetization of CeO
are modified by the irradiation with 200 MeV Xe ions. Under the assumption that these modifications are induced in the narrow one-dimensional region (the ion track) along the ion beam path, the dependence of the lattice constant and the saturation magnetization of CeO on the Xe ion fluence can be analyzed by using the Poisson distribution function. The analysis reveals that the lattice constant inside the ion track, which is larger than outside the ion track is not affected by the overlapping of the ion track. The present result implies that the Poisson distribution function is useful for describing the effect of ion track overlapping on the ion irradiation induced ferromagnetic state in CeO
on the Xe ion fluence can be analyzed by using the Poisson distribution function. The analysis reveals that the lattice constant inside the ion track, which is larger than outside the ion track is not affected by the overlapping of the ion track. The present result implies that the Poisson distribution function is useful for describing the effect of ion track overlapping on the ion irradiation induced ferromagnetic state in CeO .
.
Okayasu, Satoru; Harii, Kazuya*; Kobata, Masaaki; Yoshii, Kenji; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Ishida, Masahiko*; Ieda, Junichi; Saito, Eiji
Journal of Applied Physics, 128(8), p.083902_1 - 083902_7, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:19.49(Physics, Applied)Okuno, Yasuki*; Ishikawa, Norito; Akiyoshi, Masafumi*; Ando, Hirokazu*; Harumoto, Masaki*; Imaizumi, Mitsuru*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 59(7), p.074001_1 - 074001_7, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:19.49(Physics, Applied)Performance degradation prediction for space solar cells under irradiation with low-energy electrons is greatly affected by displacement threshold energy (Ed) when a displacement damage dose (DDD) model is used. According to recent studies, the Ed of P atoms is much lower than the conventional Ed value in InP-type solar cells irradiated with low-energy electrons. This indicates that the value of Ed typically used in DDD model leads to significant error in performance degradation prediction. In this study, degradation of AlInGaP solar cells is observed after irradiation with 60 keV electrons. The results suggest that the Ed of P atoms in AlInGaP solar cells is much smaller than the conventionally used Ed value. By using the DDD model with the Ed value obtained in this study, we demonstrated that the performance degradation predicted by the DDD model agrees well with the experimental results.
 and amorphizable Y
and amorphizable Y Al
Al O
O (YAG) crystals
(YAG) crystalsAmekura, Hiroshi*; Li, R.*; Okubo, Nariaki; Ishikawa, Norito; Chen, F.*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 474, p.78 - 82, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:53.85(Instruments & Instrumentation)Yttrium-aluminum-garnet (YAG) and calcium fluoride (CaF ) were irradiated with 200 MeV Xe ions. YAG crystal was transformed to an amorphous phase, whereas CaF
) were irradiated with 200 MeV Xe ions. YAG crystal was transformed to an amorphous phase, whereas CaF shows the non-amorphizable nature. In spite of amorphization, YAG maintained its transparency, whereas CaF
shows the non-amorphizable nature. In spite of amorphization, YAG maintained its transparency, whereas CaF markedly loses it transparency showing a broad absorption band centered at 550 nm.
markedly loses it transparency showing a broad absorption band centered at 550 nm.
 and 200 MeV Xe ion irradiation
and 200 MeV Xe ion irradiationLi, R.*; Narumi, Kazumasa*; Chiba, Atsuya*; Hirano, Yu*; Tsuya, Daiju*; Yamamoto, Shunya*; Saito, Yuichi*; Okubo, Nariaki; Ishikawa, Norito; Pang, C.*; et al.
Nanotechnology, 31(26), p.265606_1 - 265606_9, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:33.01(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)We report the elongation of embedded Au nanoparticles (NPs) in three different matrices under irradiations of 4 MeV C ions and 200 MeV Xe ions. Large elongation of Au NPs was observed for crystalline indium tin oxide (ITO) under both 4 MeV C
ions and 200 MeV Xe ions. Large elongation of Au NPs was observed for crystalline indium tin oxide (ITO) under both 4 MeV C and 200 MeV Xe irradiation. The ITO layer preserved the crystallinity even after large elongation was induced. This is the first report of the elongation of metal NPs in a crystalline matrix.
and 200 MeV Xe irradiation. The ITO layer preserved the crystallinity even after large elongation was induced. This is the first report of the elongation of metal NPs in a crystalline matrix.
 irradiation
irradiationOkazaki, Hiroyuki*; Kakitani, Kenta*; Kimata, Tetsuya*; Idesaki, Akira*; Koshikawa, Hiroshi*; Matsumura, Daiju; Yamamoto, Shunya*; Yamaki, Tetsuya*
Journal of Chemical Physics, 152(12), p.124708_1 - 124708_5, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:25.92(Chemistry, Physical)Sueyoshi, Tetsuro*; Kotaki, Tetsuya*; Furuki, Yuichi*; Fujiyoshi, Takanori*; Semboshi, Satoshi*; Ozaki, Toshinori*; Sakane, Hitoshi*; Kudo, Masaki*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Ishikawa, Norito
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 59(2), p.023001_1 - 023001_7, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:38.95(Physics, Applied)We show that Xe ion irradiation with 80 MeV to GdBa Cu
Cu Oy-coated conductors creates different morphologies of columnar defects (CDs) depending on the irradiation angles relative to the c-axis: continuous CDs with a larger diameter are formed for oblique irradiation at
Oy-coated conductors creates different morphologies of columnar defects (CDs) depending on the irradiation angles relative to the c-axis: continuous CDs with a larger diameter are formed for oblique irradiation at 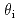 = 45
= 45 , whereas the same ion beam at a different angle (
, whereas the same ion beam at a different angle (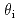 = 0
= 0 ) induces the formation of discontinuous CDs. The direction-dependent morphologies of CDs significantly affect the angular behavior of the critical current density
) induces the formation of discontinuous CDs. The direction-dependent morphologies of CDs significantly affect the angular behavior of the critical current density  .
.
 Fe
Fe O
O
Ishikawa, Norito; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*; Kitamura, Akane; Szenes, G.*; Toimil-Molares, M. E.*; Trautmann, C.*
Journal of Applied Physics, 127(5), p.055902_1 - 055902_7, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:44.34(Physics, Applied)Hillock formation is one of the important aspects of radiation-induced modification of solid material. To our knowledge this is first result showing that the hillock formation in ceramics is affected by the velocity effect. The present result include Se-dependences of hillock dimensions based on precise measurement using TEM (transmission electron microscopy). The paper should be published to make researchers aware that hillock size is actually comparable to ion-track size in wide Se range. In addition, the results include important insight about the hillock formation mechanism of ceramics irradiated with swift heavy ions.
 ; A Molecular dynamics study
; A Molecular dynamics studySasajima, Yasushi*; Ajima, Naoki*; Kaminaga, Ryuichi*; Ishikawa, Norito; Iwase, Akihiro*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 440, p.118 - 125, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:23.19(Instruments & Instrumentation)In the present paper, we have extensively analyzed the atomic structures generated by supplying a thermal spike to the single crystal CeO . Our analysis results were compared with the atomic structures obtained by the microscope experiments. Our simulation reproduced the distribution of the numbers of oxygen atoms obtained from the analysis of microscope images. We found that the number of vacancies was increased abruptly immediately after the thermal spike, and the number subsequently dropped through a relaxation process within 3 ps.
. Our analysis results were compared with the atomic structures obtained by the microscope experiments. Our simulation reproduced the distribution of the numbers of oxygen atoms obtained from the analysis of microscope images. We found that the number of vacancies was increased abruptly immediately after the thermal spike, and the number subsequently dropped through a relaxation process within 3 ps.